Fluorescent labelled vedolizumab for real-time visualization and quantification of local drug distribution and pharmacodynamics in inflammatory bowel diseases during endoscopy (VISION)
Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are chronic inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, collectively referred to as inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD). Symptoms mainly include abdominal pain, diarrhea, bloody stool, and cramps, but some patients also experience inflammatory responses in joints, eyes, skin, or the liver. Extensive morbidity has been associated with societal burden due to pain, anxiety, and depression. Medical treatment consists of aminosalicylates, corticosteroids, immune modulators, and biological agents to induce and maintain clinical remission and ultimately mucosal healing. Vedolizumab is a monoclonal antibody that blocks integrin α4β7 inhibiting trafficking of T-lymphocytes into the gut. Unfortunately, up to 60% of vedolizumab patients experience non-response. The mechanism of action of vedolizumab is not elucidated, predictors of response are unknown and data for local drug distribution in the gut are lacking. In this clinical trial, we investigate the feasibility of assessing local distribution of fluorescently labeled vedolizumab in the gut mucosa of IBD patients to finally enable prediction of therapy response in individual patients.
Study design
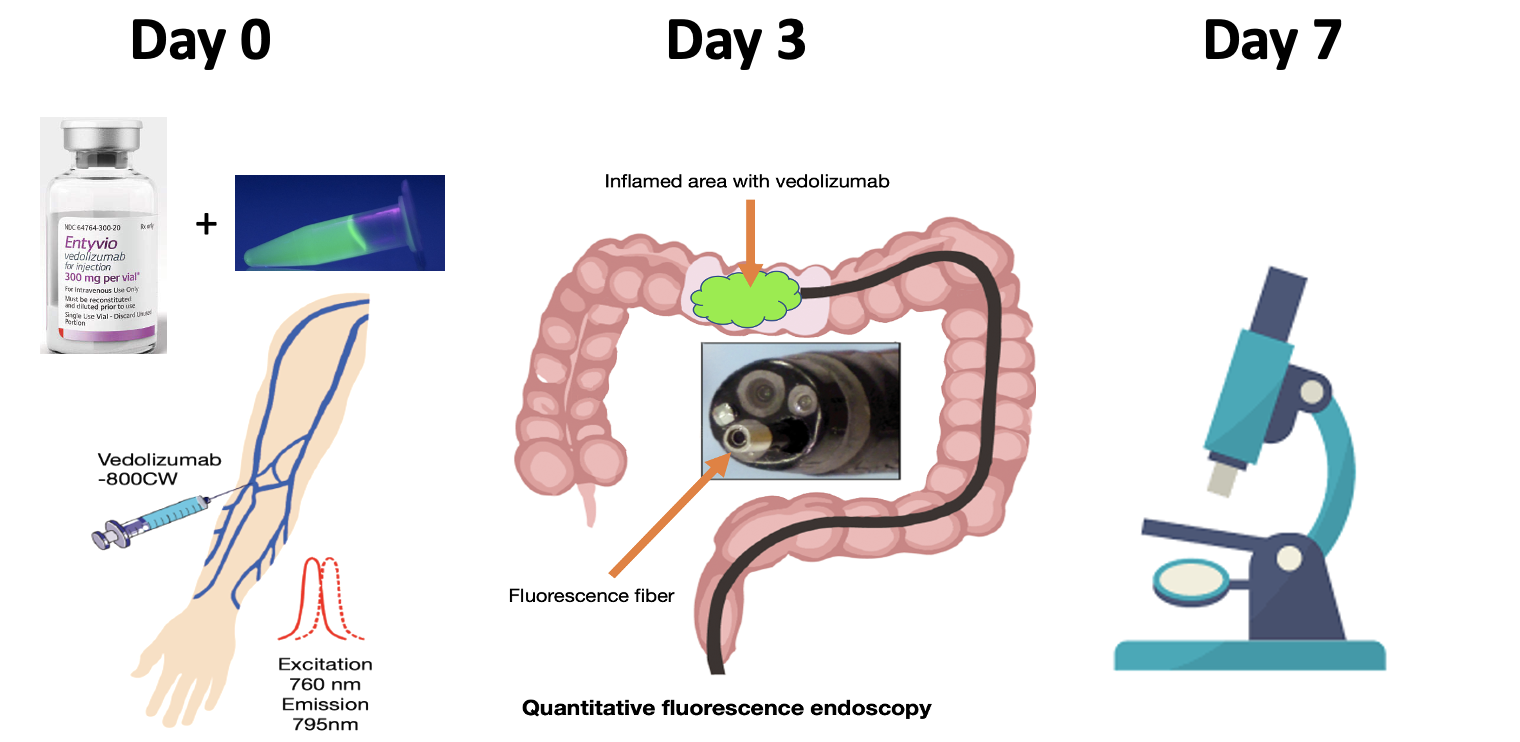
Vedolizumab (Entyvio, Takeda Pharma) was labelled to IRDye 800CW under cGMP conditions to yield clinical grade vedolizumab-800CW. Vedolizumab naïve IBD patients were included in this dose-escalation trial. Patients received an intravenous dose of fluorescently labelled vedolizumab of either 0 mg, 4.5 mg, 15 mg or 15 mg + 75 mg unlabelled vedolizumab 3 days prior colonoscopy. In vivo fluorescence imaging was assessed by fibre-based wide-field fluorescence molecular endoscopy (FME) and quantified by spectroscopy in healthy, mildly inflamed and severely inflamed tissue. All assessed tissue was biopsied for histopathological confirmation of the inflammation status, ex vivo examination of the fluorescent signal and fluorescence microscopy.
Results
Preliminary results show in vivo visualization of fluorescent vedolizumab and additional experiments to detect vedolizumab target cells are ongoing.
